

Document Type : Original Article
Authors
Department of Animal Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran
Abstract
Keywords
Bovine coronavirus is classified in the family Coronaviridae and specie of Betacoronavirus 1 group; with a diameter of 120-150 nm, and a positive sense single-stranded RNA, a human and animal pathogen that has always been characterized by high economic damage caused by diseases in its host [1]. This virus is the main cause of severe diarrhea in newborn calves. Additionally, it is associated with winter diarrhea in adult cows, respiratory infections in fattening cows, in addition to intestinal infections in cattle and wild ruminants which eventually causes severe losses to both dairy and fattening cattle sectors worldwide [2-5]
One of the relatively new areas of bioinformatics under the structural and modeling bioinformatics domain is the field of molecular dynamics simulation that has begun to flourish since the 70s [6]. These chemo-informatic simulations are widely used in drug design and structure optimization [7].
Lactoferrin is a glycoprotein present in leukocytes and known for its biological properties [8][9] such as its antibacterial [10], and antiviral [11] effects. Camel lactoferrin consists of 689 amino acids and 17 disulfide bridges. This protein has four glycosylation sites, one in the N lobe and three in the C lobe with a disulfide bond pattern similar to that of other lactoferrins found in human and horse; however, the predicted locations of glycosylation sites are quite different and with higher biological activity [12]. The potent chimeric peptide, which has been recently derived from camel lactoferrin (cLF36), has shown promising activity as an antibacterial [13], and anticancer agent [14]. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the interaction between the peptide cLF36 and the coronavirus protein to investigate its antiviral activity by utilizing computational methods.
S protein is an important component in virus entry and pathogenesis. Another importance of the S protein is its antigenicity. Antibodies induced by the S protein are highly neutralizing and are more stable during infection than those induced by the hemagglutinin-esterase protein [15]. This protein contains an N-terminal signal peptide which primes the nascent polyprotein for import into the ER. In the ER, the S protein is extensively modified with N-linked glycans, which may provide protection against neutralizing antibodies [16].
Bovine coronavirus amino acid sequence registered at the NCBI database (Accession number AAZ95502.1) was obtained in FASTA format. Then, coronavirus spike glycoprotein(S) amino acids were acquired from the NCBI. The same tool was then used to search against the PDB database and a suitable Bovine coronavirus pattern with a similarity of 94%, and overlapping of 95% was obtained under the PDB id (4H14_A). This protein was used as a template structure for 3D modeling of bovine coronavirus.
4H14_A sequence was modeled using SWISS-MODEL [17] and downloaded in PDB format. The YASARA (Yet Another Scientific Artificial Reality Application) [18] was used to optimize the energy structure of the model. Additionally, SAVES [19] was used to verify protein structure, and the best-predicted structures were selected and used in the following stage.
The predicted interaction between CLF36 and the selected protein model was investigated using ClusPro 2.0 [20] and the best model with the most negative center score was selected. Molecular dynamics simulation procedure was carried out using the GROMACS package, which consisted of GRO file preparation, solvent addition, electronic charge neutralization, system energy minimization, temperature and pressure control, and the md file generating.
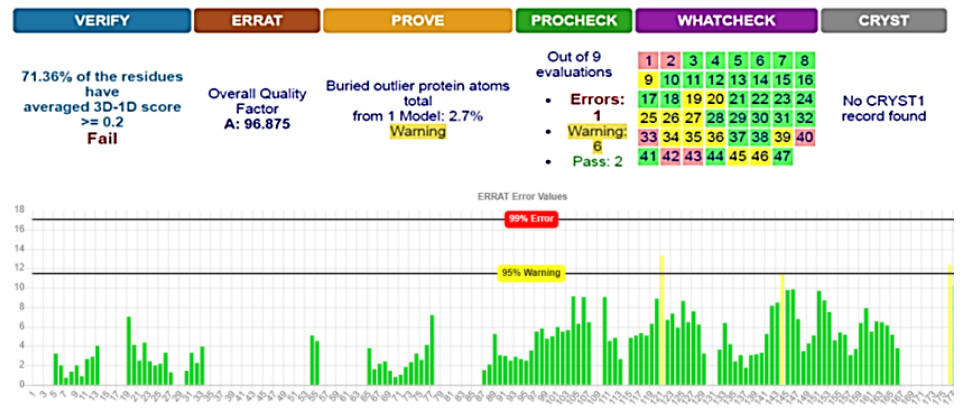
SWISS-MODEL predicted 3D structure results showed that there were 27 patterns and the best structure for our protein was 4H14_A, which was downloaded and saved in FASTA format and 3D photo [21]. Energy minimization was executed on YASARA server to obtain an optimized model structure with -23619 Kj/mol of initial energy to a final energy of -30920 Kj/mol. The energy minimized model of 4H14_A fusion protein was considered for structural validation studies by various online tools and software like PROCHECK, ERRAT, and PROVE [22][23]. SAVES results showed that the model was better before the implementation of YASARA; therefore, the first model was used for the docking phase (Fig. 1).
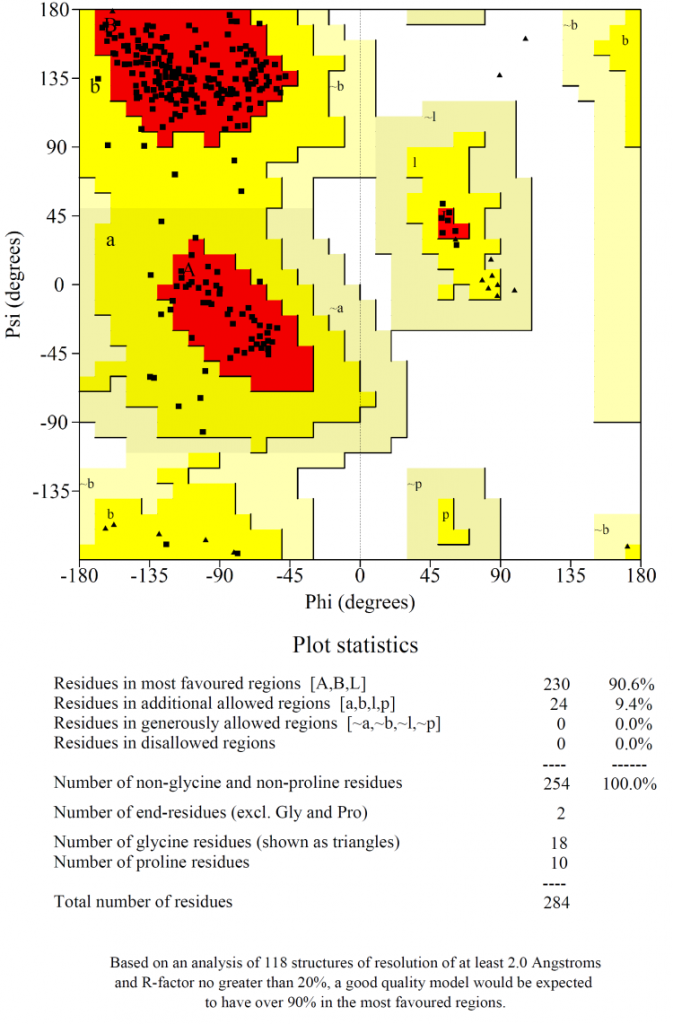
Ramachandran plot (Fig. 2) showed that 90% of the amino acids in the selected model were plotted in the most favoured region with no residues in the disallowed regions, which indicated that the chosen model was of high quality.
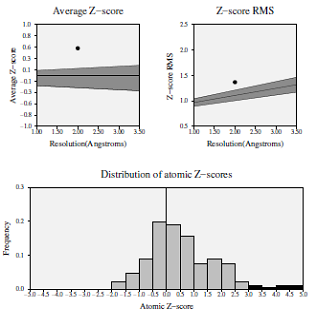
Z-score deviation analysis for the modeled protein demonstrated that the average statistical Z-score value was 0.535, which showed good results (Fig. 3) [19]
The overall estimated quality factor of ERRAT was 96.875 which is evocative of the fact that the structure is of good quality having high resolution with insignificant error standards of individual amino acid residues in modeled protein [25] (Fig. 1)
ClusPro 2.0 docking showed that the lowest energy level was - 854.6 which was attributed to complex (no.9), which was considered the best complex. The amount of complex energy was calculated based on the following formula [20]:
![]()
and showed that links lengths between the selected model and the peptide ranged between 1.7Å and 2.5Å (Fig. 4 A). These results indicated that there was a strong association between coronavirus peptide and cLF36 [26].
GROMACS results showed that the electrical charge was positive (10.99). Energy minimization was achieved reaching the 729 phase. Xmgrace results showed that the system was in equilibrium in terms of temperature and pressure and the final structure (Fig. 4 B) illustrated that the relationship between the two proteins was strong and robust. Therefore, this system can be suggested as a suitable model in drug design.
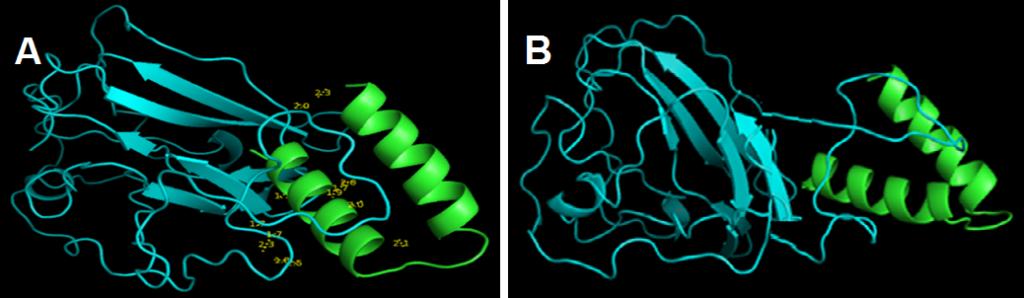
Figure 4. Docking results between the protein model (blue) and cLF36 (Green)(A) and the final structure of the system from Gromax (B). The link length ranged between 1.7Å and 2.5Å indicating a strong predicted association between the protein model and cLF36.
Bovine coronavirus is a livestock pathogen that has always been known to cause high economic losses. In this study, the association between engineered cLF36 peptide and bovine coronavirus protein was assessed computationally. The results showed that the best complex with the lowest binding energy and connection between the two proteins was strong (1.7-2.5 Å) which is close to reality. Further laboratory tests are required for final approval of cLF36 peptide in the fight against calf diarrhea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Funding statement
The authors declared that no funding was received in relation to this manuscript.
Data availability statement
The authors declared that all related data are included in the article.